Project Managers have lot of
responsibility for the success or failure of the project.
Managing a project in general is
different than managing in general. PM is the person everyone looks for the
solution.
One of the key challenges for PM
is the entire accountability but lack of authority.
Another challenge for PMs is
along with project responsibility they have "regular job' also which they
have to do.
All of these things make the PM
job a tough job.
Project Management is the
centralized – Planning, Organizing, Controlling & Monitoring of key
activities to ensure project objectives and customer satisfaction meet.
Project Management means –
Managing the team, time, resources, within budget and meeting all requirement
specifications.
To do this, there are four key
stages in any project – Initiating, Planning, Executing and Closing.
Responsibilities:
PM responsibility lies into
various phases – Initiating, Planning, Executing, Controlling & Closing.
Initiating:
Envisioning and Initiating:
Project Charter / Project
Initiation Document & Business Case:
Document Project Purpose or Objectives,
Documents the Business Need/Case
High-level Project Description,
Generate High-level
Requirements,
Generate Initial Traceability
Matrix
Generate Initial Estimates /
Summary Budget - DRCP
Generate Initial Project Schedule
/ Summary Milestone Schedule
Generate Project Plan
Generate High-level Risks,
Prepare Project Scope,
Generate Project Deliverables,
Generate Project Constraints
& Assumptions
Generate QA Concept Report
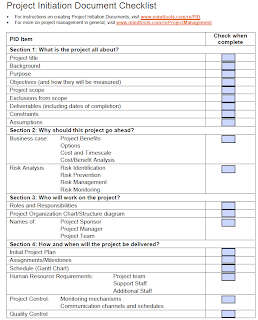
All of this information should
gather in PID/Charter document as below.
Requirements
Baseline: Able to facilitate
proof-of-concept, prototyping, interviewing/workshops or other techniques of
gathering requirements.
Core
Team/Team Charter:
Able to develop an organizational chart (OBS) for the core team based on the
roles and responsibilities of the stakeholders.
Identify
Stakeholders & Stakeholder Management Strategy - RACI Chart
Planning:
Project Planning is
crucial to project. This involves:
Detailed Requirement Gathering – Functional Specifications &
Use Cases
Define Scope & Scope Breakdown(WBS)
Define Activities & Micro Estimation
- HD Effort
Estimation Excel Template
Estimate Activity Durations – HD Effort Estimation Excel
Template
Estimate Resources – Same - HD Effort Estimation Excel
Template
Re-Define Project Cost &
Budget – DRCP
Sequence Activities &
Re-Create Project Schedule and Assign Resources – MPP
Project Plan
Overview
Purpose scope and objectives
Project Objective/Goal and
priority
Deliverable
Success Criteria
Assumptions & Constraints
Project Organization
Project Team Structure
Roles and Responsibilities
Staffing
Project Staff Training
Stakeholder and User Involvement
Project Governance
Project Monitoring and Control
Others
Re-Risk Identification
Plan Communication
Plan Configuration
Quality Planning
Measurement Plan – Project Metrics
Milestones
Environment Definitions
CAR
DAR
Testing Approach
End User Training
Deployment Strategy and Approach
Develop Final Project Plan and
Gain Formal Acceptance
CMMi Process:
Project Sizing
Effort Estimation – Thru PPM
(CMMi)
Prepare Initial Capital &
Estimation
Sequence Activities &
Create Project Schedule - MPP
Statement of work (SOW):
Scope Statement and Baseline: Ensures the scope statement is
clearly understood and as agreed to by the project team, customer, and other
stakeholders, creates the scope baseline, and the process for scope change
control.
Scope Breakdown: Applies decomposition
techniques to document breakdown structures that break-up the deliverable into
work packages that can be estimated and to facilitate risk assessment.
Project Plan: Ensures that the project plan
is complete, and determines the overall project management plan for use in
managing and controlling during project execution.
SOW (Schedule and Cost):
Task and Duration Estimating: Able to create tasks and their
sequence given the scope statement/description of services at sufficient enough
detail for duration estimate to be developed.
Schedule Development and Baseline: Able to select and perform
appropriate mathematical analysis (e.g. critical path method, schedule
optimization), gain acceptance, create the schedule baseline, and the process
for schedule change control.
Cost Development and Baseline: Able to allocate overall costs
to tasks, associate any billing codes, gain acceptance, create the cost
baseline and the process for cost change control.
SOW (Resource and Planning):
Resource Plan: Able to develop the resource
plan addressing how resources are brought onto and taken off the project as
supporting detail to the project plan.
Resource Acquisition: Able to execute the staffing
management plan and allocate staff communicating responsibilities, authority,
performance measurement criteria, and overall project goals and vision.
Communications Plan: Establish a plan for
time-reporting and project status reporting processes, managing the
dissemination of routine and non-routine communications including publication
cycles.
Communications Infrastructure: Able to execute the
communications plan including user acceptance and training sufficient to ensure
internal and external reporting/communications will be met.
SOW (Risk Management and
Quality):
Risk Assessment and Risk Plan: Able to identify roles, assign
risk owners, responsibilities and levels of authority for management and
decision-making, develop contingency plans, implementation criteria, and
alternatives strategies as supporting detail to the project plan.
Risk Management and Reporting: Able to execute the risk plan,
implement corrective action, mitigation, workarounds, update the plan and
report status.
Quality Plan: Able to develop a quality plan
addressing metrics, productivity, rework, and any processes or standards are
developed to increase stakeholder satisfaction as supporting detail to the
project plan.
Quality Management and Reporting: Able to execute the quality
plan, perform inspections, reviews, and walk throughs to ensure quality efforts
meet compliance in accepted, rejected, or rework criteria, update the plan and
report status.
Executing & Controlling:
Performance, Benchmarking and
Closing:
Project Performance Management
and Reporting: Able to execute the
project plan, implement mechanisms to measure, record progress, and conduct
ongoing analysis of variances, risks, and changes, as well as update/revise the
project plan and report status.
Change Management and Reporting: Able to gain approvals to
change requests, re-baseline when applicable, update/revise the project plan
and report status.